What is proper treatment of industrial waste?
Waste does not go away as long as we live; it is like clothing, food, and housing.
AMEC feels that in addition to achieve a final treatment to remove hazardous waste, it is essential to achieve a treatment in which industrial waste is recycled and reutilized.
- Solutions to industrial waste treatment developed and proposed by AMEC aim to upgrade and optimize intermediary industrial waste treatment by, for example, reducing the environmental load imposed on the treatment site with limited waste burial facilities and by effectively using a limited amount of resources.
- AMEC makes it possible to recycle the waste to create new resources by stabilizing the heavy metals in waste such as burned ash and sludge using our unique insolubilization technology.
- AMEC realizes advanced treatment that has long-term stability by utilizing the chemical insolubilization of inorganic waste using mainly inorganic compounds.
Specific examples of AMEC’s solutions
Our products and methods are listed below, targeting different pollution situations.
- Materials and conditions of waste:
- Burned ash
Ash, volume reduced by burning, scheduled for landfill treatment. Heavy metals are concentrated by volume reduction. - Pollutant concentration:
- Fluorine (F)
1.1mg/L
Hexavalent Chrome (Cr(Ⅵ)) 0.85mg/L - Purpose of disposal:
-
- Recycle waste
- Reduce elution of fluorine and hexavalent chrome down to less than environmental limit and reuse it as roadbed and backfill materials.
- Method and materials:
- Insolubilization AC-1
- Reasons why AMEC was chosen:
- Capable of handling multiple kinds of elements. Low cost treatment with a smaller additive amount compared with existing treatment materials.
- Achievements:
- Adopted in industrial waste treatment project in Shikoku
- Materials and conditions of waste:
- Burned ash
Ash, volume reduced by burning, scheduled for landfill treatment. Heavy metals are concentrated by volume reduction. - Pollutant concentration:
- Lead (Pb) 3.1mg/L
- Purpose of disposal:
-
- Improve safety of waste
- Reduce lead down to less than the environmental limit; use landfill treatment in waste treatment sites.
- Method and materials:
- Insolubilization Ash Claw (type S for burned ash)
- Reasons why AMEC was chosen:
- Capable of controlling variable volume of elution from burning non-industrial waste down to less than the standard while always using a constant additive amount.
- Achievements:
- Adopted in non-industrial waste treatment site in Shikoku
- Materials and conditions of waste:
- Paper sludge ash
Ash created by burning the waste from a paper manufacturing process. Basically scheduled for landfill treatment. - Pollutant concentration:
- Fluorine (F) 1.2~7.0mg/L
Boron (B) 4.2mg/L - Purpose of disposal:
-
- Recycle waste
- Reduce fluorine and boron down to less than the environmental limit.
Reuse as backfill material or for adjusting the water content of sludge.
- Method and materials:
- Insolubilization AC-1
- Reasons why AMEC was chosen:
- Capable of controlling a variable volume of elution down to less than the standard while using a constant additive amount. Insolubilization materials for existing facilities can be used.
- Achievements:
- Adopted, on a trial basis, in industrial waste treatment project in Shikoku
- Materials and conditions of waste:
- Oxide slag
Waste containing heavy metals from stainless steel production. - Pollutant concentration:
- Fluorine (F) 5.6mg/L
Selenium (Se) 0.056mg/L
Hexavalent Chrome (Cr(Ⅵ)) 0.06mg/L - Purpose of disposal:
-
- Recycle waste
- Reduce fluorine, selenium, and hexavalent chrome down to less than the environmental limit; reuse as roadbed materials.
- Method and materials:
- Insolubilization AC-1
- Reasons why AMEC was chosen:
- Capable of handling multiple kinds of elements. In addition to the suppression of elution, a moderate increase in strength is achieved.
- Achievements:
- Adopted in the field test of the metal-processing industry in Chubu District.
- Materials and conditions of waste:
- Dust from melt treatment
Waste from a melting treatment containing heavy metals - Pollutant concentration:
- Lead (Pb) 2.1mg/L
Cadmium (Cd)14mg/L - Purpose of disposal:
-
- Reduce load imposed on waste treatment sites
- Reduce elution concentration of lead and cadmium, exceeding the disposal standard of specially controlled waste, down to less than the environment standard. Reduce discharge costs.
- Method and materials:
- Insolubilization AC-1
- Reasons why AMEC was chosen:
- Treatment reliably reduces high concentration of lead and cadmium down to less than the standard.
- Achievements:
- Adopted in a laboratory test of metal-processing industry in Chubu District
Description of methods
~comparison of countermeasure methods~
AMEC aims at reliable and robust stabilization using chemical reactions.
In addition, it is basically possible that the treatment will not substantially change the characteristics of the target and will not affect its future use.
Physical solidification method
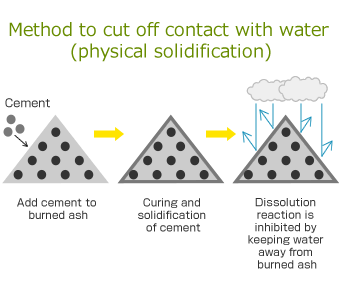
- Summary:
- Mainly using cement, this method suppresses the elution of heavy metals by solidifying the target material. Contact with water is cut off so that the elution of heavy metals is suppressed.
- Curing:
- Necessary
- Material use:
- High
- Economic potential:
- ◯
- Stability:
- ×
- Environ-mental load:
- △
Adsorption and insolubilization method
(AMEC)
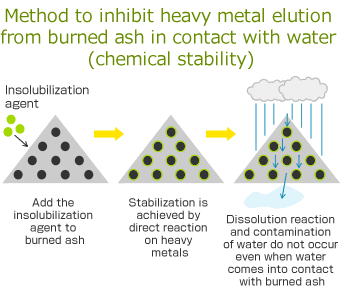
- Summary:
- Heavy metals are chemically solidified and stabilized by adding adsorbent and insolubilization materials to the contaminated soil and by evoking a reaction. Without the need to prevent contact with water, the treatment can proceed without substantially changing the characteristics of the target. Recycling of resources is possible after reducing the elution concentration below the standard.
- Curing:
- Unnecessary
- Material use:
- Low
- Economic potential:
- ◯
- Stability:
- ◎
- Environ-mental load:
- ◯
Steps toward the solution of the problem
AMEC’s sales representatives and engineers brainstorm in consultation with the customer until a satisfactory solution is reached.
- 1Emergence of a problem
- Do not hesitate to contact AMEC when in urgent need of pollution countermeasures.
- 2Diagnosis
- A sales representative and an engineer are specislly assigned to each cutomer;they are responsible for helping thecustomer to solve the problem.
- 3Vaidation
- They examine the on-site and surrounding environment and take note of the customer's problems.
- 4Planning
- AMEC's engineers work together to find the best suitable solution and draw up a plan.
- 5Solution to the problem
- We make every effort to not only clean up the pollution but also ease the customer's concerns.
